Representation:
- Revealing clothing
- Sexualized
- Women should be submissive
- Short temper
- Wives + Mums
- Secondary roles
Representation:
is how media texts deal with and present
gender, age, ethnicity, national and regional identity, social issues and
events to an audience.
Stereotypes: are a simplified representation of a person,
groups of people or a place, through basic or obvious characteristics - which
are often exaggerated.
Counter-stereotypes: A counter-stereotype is an idea or object that goes against a standardized mental picture that is held in common by members of a group and that represents an oversimplified opinion, prejudiced attitude, or uncritical judgment.
Countertype:
Focuses on positive elements of a group traditionally represented as bad.
Anchorage:
Words that go along with images to give meaning
to them in a specific context; includes captions in newspapers and taglines on
film posters.
Van zoonen theory:
Van
Zoonen
believes the media portray images of stereotypical women and this behaviour
reinforces societal views. The media does this because they believe it reflects
dominant social values (what people believe in) and male producers are
influenced by this. This is a patriarchy (a society ran by men for men) which
dominates and oppresses women.
In patriarchal culture, the way women’s
bodies are represented as objects is different to the representation of male
bodies as spectacle.
Gender is performative – our ideas of
femininity and masculinity are constructed in our performances of these roles.
Gender is ‘what we do’ rather than ‘what we are’. Moreover, gender is
contextual – its meaning changes with cultural and historical contexts.
Van Zoonen stereotypical
presentations:
Feminine - Masculine
Caring - Careless
Nurturing - Impatient
Unreasonable - Rational
Private - Public, Work-orientated
Sensitive - Domesticated
Lazy - Active
Gentle - Rough
Soft - Tough
Feminity & Stereotypes in the music video "Wrecking ball" - Miley Cyrus:
- Red lips
- Barely any clothes (underwear or naked)
- Crying (Emotional - like the song)
- Close frame
- Blonde hair
Vs
- Short hair
- Boots
- Destruction (Manly) - Wrecking ball
- Physical
- Independence
Representations of Masculinity/Men:
- Strength (Physical & Intellectual)
- Power
- Sexual attractiveness
- Physique
- Independence
Representation of Femininity/Women:
- Beauty
- Size/Physique
- Emotional (Apposed to intellectual)
- Relationships (Upposed to independence)
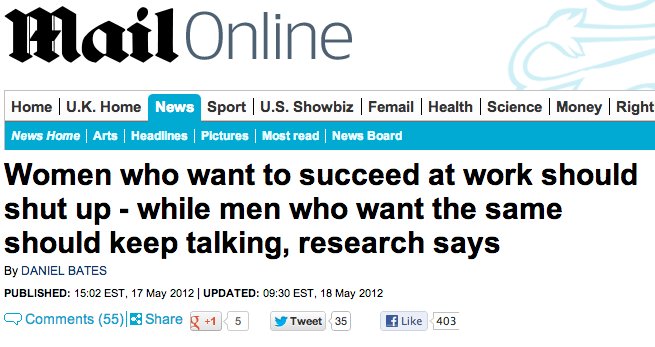
Using van Zoonen’s theory and the stereotypes associated
with gender discuss how the Daily Mail have represented gender from the two
front covers presented.
Archetype: A very typical example of a certain person/thing.
Such as; Snoop dogg and 50 cent represents criminals being black.
Demonization: Demonization is the reinterpretation of polytheistic deities as evil, lying demons by other religions, generally monotheistic and henotheistic ones. The term has since been expanded to refer to any characterization of individuals, groups, or political bodies as evil.
In this case, people of a higher class than other people, like to demonize people of lower class to make themselves feel and look better than them and make the lower classes look worse.
Hegemony:
- Gramsci’s
theory of hegemony can be visualised
as the Middle classes (media, Judges (rule of law), Public, Education sector
and religious bodies) using their influence to preserve the status quo.
- The
poor and working class are often represented in an unsympathetic /biased way
(trouble makers, deviant as a means of preserving the power of the middle and
upper class).
- This
is illustrated in the attached images
- Hegemony
(theory) does not only apply to class it is relevant to gender (patriarchy) and
race…
Regional identity:
Regional
Identity
refers to the part of the United Kingdom someone is from. It could refer
to a general area such a “North” or “South”, a
country such as “English” or “Scottish” or specific towns such as “London” or
“Manchester.”
How can you identify regional identity?
– Setting
– Accents
–
Dialogue
– Props
–
Make up
– Class of characters
– Costumes
– Etc.
North
England – often shown as being poorer, bad weather, lower class, aggressive,
less culture, less clever, doing working class jobs such as builders,
etc.
South
England – often shown as being the centre of culture, modern, classy, clever,
sunny, richer, doing middle class jobs such as managers, etc.
Essex –
often shown as being glamourous but
cheap, footballer’s wives, lots of partying, being quite stupid
Race:
Ethnicity - An ethnic group or ethnicity is a population
group whose members identify with each other on the basis of common nationality
or shared cultural traditions
Race - The term race refers to the concept of
dividing people into populations or groups on the basis of various sets of
physical characteristics (which usually result from genetic ancestry).
Key themes in racial representation:
- Exotic
- Dangerous
- Big Russian Boxer
- Very dangerous to fight
- Humorous
- Funny asian person
- Crazy
- Pitied
- Stud/Pimp
- Gangster
- Black
Islamophobia: is the fear, hatred of, or prejudice against the Islamic religion or Muslims generally, especially when seen as a geopolitical force or the source of terrorism. The meaning of the term continues to be debated, and some view it as problematic.
Class:
Working class: Those individuals engaged in manual work,
often having low levels of educational achievement. The classic, traditional
working class jobs include heavy labouring
and factory based work.
Working class (Stereotypes)
- Presented in the stereotypical context of traditional working class communities such Eastenders and Corrie, Shameless
- Community values often praised but do not reflect reality,
- Working class communities have declined with the collapse of traditional industries such as coal mining.
- Often presented in the context of trouble, undesirable welfare scroungers, unable to cope with their delinquent children.
- Poor and undeserving of sympathy
Representations of Working class
• Portrayal usually negative and stereotypical,
• Portrayal usually negative and stereotypical,
• Portrayed in the form of statistics in
news bulletin such as figures of unemployment,
• Recent media interest in the labelling of
the poor such as “chavs”
which according to Shildrick and
MacDonald (2007) suggest that the poor are undeserving of sympathy,
• Hayward and Yar
(2006) – the term chav is
used as an amusing term of abuse for young poor people
•Newman
(2006)
argues that there are very few situation comedies, television or drama which
focuses on the everyday lives of working class who constitute a significant
section of society,
•Newman
argues
that when in the media working class are often depicted in a very non positive
light dumb buffoons (Homer Simpson) and immature machos (Phil Mitchell),
•Butsch (1992)
– working class portrayed as flawed individuals (benefit cheats, etc.)
Middle class (Stereotypes)
- Presented as educated and successful as well as able to cope with problems,
- Over represented in the media due to their lifestyle
- Representation fits in with the hegemonic ideology of the dominant class in society,
- Representation justifies the existing class structure and inequalities by suggesting people need to become more competent and successful in order to cope with life.
Upper class: The elite class that controls the majority of
wealth and power in British society.
Upper class (Stereotypes)
- Presented as rich, well dressed and superior to other classes
- Intellectual, posh people who are well spoken.
- Often presented as land & high-end property owners to show wealth.